Embarking on a career path in Information Technology (IT) management can be both thrilling and daunting. As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the demand for skilled IT managers who possess a unique blend of technical expertise and leadership qualities has never been higher. In this article, we will delve into the essential qualifications required for aspiring IT managers, providing valuable insights and guidance on how to navigate this dynamic field with confidence.
Readers can expect an in-depth exploration of the key technical skills and soft skills needed to excel in the role of an IT manager. From discussing the importance of gaining relevant experience to highlighting the significance of pursuing professional certifications, we aim to equip you with the knowledge and tools necessary to carve out a successful career in IT management. Join us on this journey as we unravel the intricacies of what it takes to thrive in one of the most crucial roles within the realm of technology.
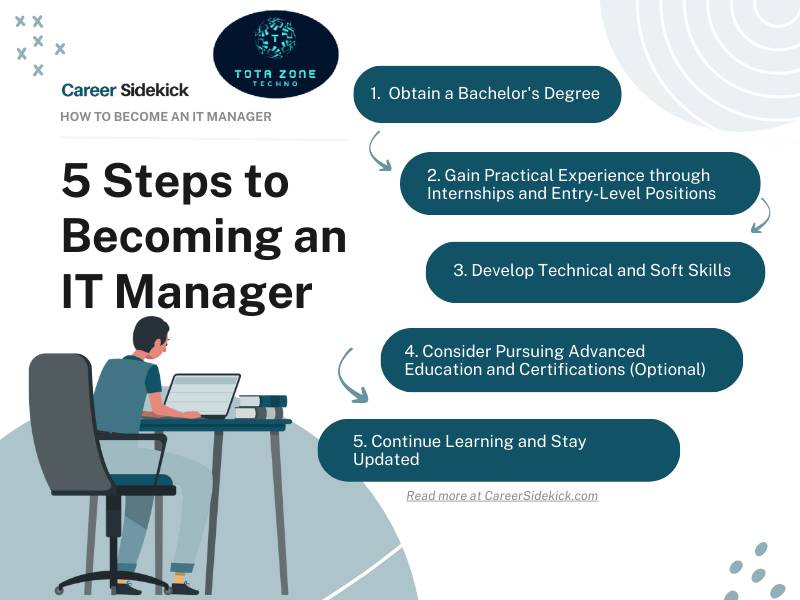
The Journey to Becoming an IT Manager
Embarking on the journey to become an IT manager is a rewarding and challenging endeavor. It requires a blend of technical expertise, leadership skills, and a passion for driving innovation in the ever-evolving realm of technology.
To start this journey, aspiring IT managers typically begin by pursuing a bachelor’s degree in a relevant field such as computer science, information technology, or engineering. This educational foundation provides them with essential knowledge in areas like programming, networking, databases, and systems analysis.
After completing their academic studies, individuals interested in becoming IT managers often gain practical experience by working in entry-level positions such as help desk support or junior developer roles. This hands-on experience allows them to understand the intricacies of IT operations and hone their technical skills while learning about different aspects of managing technology within an organization.
As they progress in their careers, aspiring IT managers may seek out opportunities to take on leadership roles within project teams or cross-functional initiatives. By demonstrating strong communication skills, problem-solving abilities, and a knack for collaborating with diverse stakeholders, they can showcase their potential for leading larger teams and overseeing complex technical projects.
Understanding the Role of an IT Manager
As the linchpin between technical teams and business objectives, an IT Manager plays a crucial role in organizations. They are responsible for overseeing the planning, implementation, and maintenance of information technology systems. Beyond technical expertise, IT Managers must possess strong leadership skills to effectively manage teams and drive projects to success.
IT Managers are not just problem-solvers; they are strategic thinkers who align technology initiatives with the overall goals of the organization. They must have a deep understanding of how technology can impact business operations and be able to communicate this effectively to stakeholders at all levels. This role requires a blend of technical acumen and business acumen to make informed decisions that drive innovation.
One key aspect of an IT Manager’s role is managing resources efficiently. This involves not only overseeing budgets and timelines but also optimizing team performance to ensure projects are delivered on time and within scope. Effective communication is essential in this aspect, as IT Managers must relay expectations clearly while motivating their teams towards achieving common goals.
In addition to overseeing day-to-day operations, IT Managers also play a critical role in fostering a culture of collaboration and continuous improvement within their teams. By promoting knowledge sharing, encouraging professional development, and providing mentorship opportunities, they create an environment where team members can thrive and contribute meaningfully towards organizational success.
Key Technical Skills Required
Cybersecurity Knowledge: In today’s digital landscape, IT managers must have a deep understanding of cybersecurity principles to protect their organization’s data and systems from potential threats. Proficiency in areas such as network security, encryption methods, and threat detection is crucial for building a secure IT infrastructure.
Cloud Computing Expertise: As more businesses migrate to cloud-based systems, IT managers need to be well-versed in cloud computing technologies like AWS, Azure, or Google Cloud. Understanding how to leverage cloud services for scalability, cost-efficiency, and data storage is essential for modern IT management.
Data Analysis Skills: The ability to analyze and interpret complex data sets is becoming increasingly important for IT managers. Proficiency in data analytics tools like SQL or Python allows them to make informed decisions based on trends and patterns within the organization’s data, driving strategic initiatives forward.
Project Management Abilities: Effective project management skills are vital for overseeing the successful implementation of IT projects within budget and timeline constraints. From planning and resource allocation to risk management and stakeholder communication, IT managers must possess strong project management abilities to ensure project success.
Essential Soft Skills for Success
Soft skills play a crucial role in the success of an IT manager. Communication skills are paramount, as IT managers need to effectively convey complex technical information to non-technical stakeholders. Additionally, leadership and team management skills are essential for guiding and inspiring their teams towards common goals.
Empathy is another important soft skill for IT managers, as it allows them to understand the perspectives and needs of their team members, fostering a positive work environment. Adaptability is key in the ever-evolving IT landscape, enabling managers to navigate unexpected challenges and changes with ease.
Problem-solving skills are highly valued in IT managers, as they must be able to analyze issues, devise innovative solutions, and implement them efficiently. Time management is also critical for overseeing multiple projects simultaneously while ensuring deadlines are met consistently.
Creativity rounds out the set of essential soft skills for IT managers by enabling them to think outside the box when approaching complex problems or designing strategic initiatives. These soft skills collectively form a solid foundation for IT managers to excel in their roles and drive success within their teams.
Gaining Relevant Experience
Experience is crucial for aspiring IT managers to develop a comprehensive understanding of the industry and hone their skills. One effective way to gain relevant experience is by starting at the grassroots level within an IT department. By working on diverse projects and collaborating with seasoned professionals, individuals can acquire valuable insights into the complexities of IT management.
Internships and apprenticeships are also excellent avenues for gaining practical experience in the field. These opportunities provide hands-on training, exposure to real-world scenarios, and a chance to work under the mentorship of experienced IT managers. By actively participating in projects, troubleshooting technical issues, and engaging with cross-functional teams, individuals can build a solid foundation for their future roles.
Furthermore, seeking out opportunities to lead smaller projects or initiatives within an organization can significantly contribute to skill development. Taking on responsibilities such as project coordination, team management, and decision-making allows individuals to showcase their leadership potential and demonstrate their ability to navigate complex IT challenges effectively.
Continuous learning through workshops, seminars, and industry conferences also plays a vital role in gaining relevant experience. Engaging with thought leaders in the field, staying abreast of technological advancements, and participating in discussions on emerging trends help individuals broaden their perspectives and enhance their expertise as they progress towards becoming proficient IT managers.
Pursuing Professional Certifications
Expanding Expertise Through Certifications: Professional certifications are valuable assets for IT managers, showcasing specialized knowledge and skills. Certifications such as CompTIA Project+, Certified Information Systems Security Professional (CISSP), and ITIL Foundation demonstrate expertise in project management, cybersecurity, and IT service management.
The Value of Continuous Learning: Pursuing certifications not only enhances technical skills but also demonstrates commitment to professional growth. Continuing education through certifications allows IT managers to stay updated with evolving technologies and industry best practices. Embracing a culture of lifelong learning is key to thriving in the dynamic field of information technology.
Certifications as Career Accelerators: Acquiring relevant certifications can open doors to new career opportunities and advancement within the IT management domain. Employers often prioritize candidates with industry-recognized certifications, viewing them as proactive professionals dedicated to staying current in their field. Securing certifications can boost confidence and credibility in one’s managerial abilities.
Networking Opportunities Through Certification Programs: Engaging in certification programs not only facilitates knowledge acquisition but also provides networking opportunities with industry peers and experts. Building connections within the professional community can lead to collaborations, mentorship opportunities, and valuable insights into emerging trends. Certifications serve as a bridge to connect with like-minded professionals passionate about excelling in IT management.
Building a Strong Professional Network
Networking is a powerful tool for IT managers to expand their knowledge, seek advice, and discover new opportunities. Cultivating relationships within the industry can lead to valuable insights and collaborations.
Start by attending industry events, conferences, and seminars to meet fellow professionals. Engage in meaningful conversations, exchange ideas, and connect with individuals who share your passion for technology.
Utilize online platforms such as LinkedIn to stay connected with colleagues, peers, and influencers in the IT field. Share your expertise through articles and posts to establish yourself as a thought leader and attract like-minded professionals.
Mentorship is another effective way to build a strong network. Seek guidance from experienced IT leaders who can offer valuable advice and support as you navigate your career path. Remember, networking is not just about making connections; it’s about fostering genuine relationships that can benefit both parties in the long run.
Navigating Career Advancement Opportunities
Continual Learning: Embrace a growth mindset by taking on new challenges and seeking out learning opportunities. Attend workshops, seminars, and industry conferences to stay ahead in the ever-evolving tech landscape. This commitment to ongoing education will not only enhance your skill set but also demonstrate your dedication to professional development.
Mentorship: Seek guidance from experienced professionals in the field who can offer valuable insights and advice on how to navigate the complexities of career advancement. A mentor can provide support, feedback, and encouragement as you strive toward reaching your goals. Remember, even the most accomplished leaders had mentors who helped shape their journey.
Networking: Cultivate meaningful relationships within the industry by networking with colleagues, attending industry events, and engaging with online communities. Building a strong professional network can open doors to new opportunities, collaborations, and mentorship connections. Remember, it’s not just about what you know but who you know that can help propel your career forward.
Promoting Visibility: Showcase your expertise by participating in speaking engagements at conferences or writing articles for industry publications. By sharing your knowledge and insights with others, you not only establish yourself as a thought leader in the field but also increase your visibility within the tech community. This increased visibility can lead to exciting career advancement prospects.
Staying updated with industry trends
As an IT manager, staying abreast of the latest industry trends is paramount to your success. Technology evolves rapidly, and being in tune with emerging technologies and market shifts can give you a competitive edge.
Continuous Learning
Embrace a mindset of lifelong learning to stay relevant in the ever-changing IT landscape. Attend industry conferences, workshops, and webinars to expand your knowledge base. Engage with online forums and communities to discuss trends and innovations with like-minded professionals.
Networking Opportunities
Networking is not just about making connections; it’s about gaining insights into what’s happening in the industry. Attend networking events and meetups to interact with peers, share ideas, and glean valuable information about upcoming trends that could impact your role as an IT manager.
Industry Publications
Subscribe to reputable tech publications and blogs to access insightful articles, reports, and analysis on current industry trends. Reading thought leadership pieces can broaden your perspective and provide valuable foresight into where the industry is heading.
Mentorship and Collaboration
Engage in mentorship relationships or collaborative projects with experienced professionals in the field. Learning from seasoned experts can offer unique perspectives on emerging trends and best practices, helping you adapt proactively to changes in the IT landscape.
Conclusion
As the technology landscape continues to evolve rapidly, the role of an IT manager remains crucial in organizations worldwide. By honing a diverse skill set comprising technical expertise, strategic thinking, and effective communication, aspiring IT managers can position themselves for success in this dynamic field. Embracing continuous learning and adapting to emerging trends will not only enhance professional growth but also contribute to shaping the future of technology management.